It has been well documented that companies maintaining continued success in public procurement, also enjoy more predictability in their cash flow, and are generally more financially stable in insecure times. As discovered in our Government Receivables as a Stock Market Signal white paper, winning government contracts is also likely to have a positive impact on a company’s stock price.
Therefore, we thought it would benefit our readers if we offered them detailed analyses of the financial results these major government contractors achieve.
It is now time for us to look again at a company we covered previously in this series. Siemens recently reported its H1 2024 results and below we will provide a brief analysis of the company’s performance in the first 6 months of the year.
Key points:
* Mobility and Siemens Healthineers segments rely heavily on government orders. They accounted for a combined 43% of H1 2024 revenue;
* Consolidated H1 2024 revenue was flat Y/Y, with 6% growth targeted for the full year;
* EPS pre PPA of €5.92/share in H1 2024 was down 11% Y/Y, with a smaller 1% decline forecast for the full year;
* Backlog up 3% since September 2023, with a book-to-bill ratio of 1.14;
* Siemens is selling Innomotics for €3.5 billion.
Siemens H1 2024 Results Overview
Siemens has a fiscal year ending on September 30. We previously covered Siemens’s Q1 2023 results in part 21 of our Top Government Contractors series here. Below we will highlight the progress achieved by the company in the first half of its fiscal 2024.
The company's core Industrial Business (94% of H1 2024 revenue) is subdivided into Digital Industries at 24% of H1 2024 revenue, Siemens Healthineers at 28%, Smart Infrastructure at 26% and Mobility at 15% of fiscal H1 2024 revenue:
Figure 1: Siemens H1 2024 revenue by segment
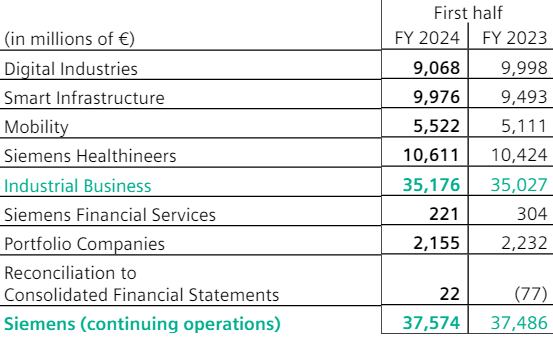
Source: Siemens H1 2024 Financial Report
From a geographic perspective, the company derived 48% of its H1 2024 revenue from Europe, C.I.S., Africa, and the Middle East, 30% from the Americas, and 22% from Asia and Australia.
Operational Overview
Digital Industries was the only segment to record a revenue decline in H1 2024, with sales decreasing 9% Y/Y. The weak performance was driven by lower demand in the high-margin automation businesses, partially offset by strength in software. This led to weaker profit margins, at just 18% (H1 2023: 23.8%).
Smart Infrastructure was the second-best performing segment, growing its topline by 5% Y/Y in H1 2024. The strong performance was due to elevated demand in the U.S. for electrification businesses, particularly in data centers. Higher sales led to better capacity utilization which coupled with productivity improvements pushed margins to 17.4% (H1 2023: 15.6%).
Mobility was the fastest growing segment, up 8% Y/Y, with growth across all business sub-segments. Profit margins were marginally higher, at 8.8% (H1 2023: 8.6%).
Siemens Healthineers delivered 2% revenue growth in H1 2024, with margins recovering to 12.9% (H1 2023: 8.9%) on the non-recurrence of one-off charges recorded in the prior-year period, as well as broad-based volume growth.
On a consolidated level, revenue was flat Y/Y (2023: +8%), EPS pre PPA (defined as basic earnings per share from net income adjusted for amortization of intangible assets acquired in business combinations and related income taxes) was down 11% Y/Y to €5.92/share on lower contribution from non-industrial businesses. The industrial business profit margin was 14.9%, flat Y/Y. Free cash flow was €2.4 billion, flat Y/Y.
Updated 2024 Outlook
Siemens largely confirmed its initial 2024 outlook, with a stronger-than-forecast decline in the Digital Industries segment offset by better results in Smart Infrastructure:
Figure 2: Siemens updated 2024 outlook
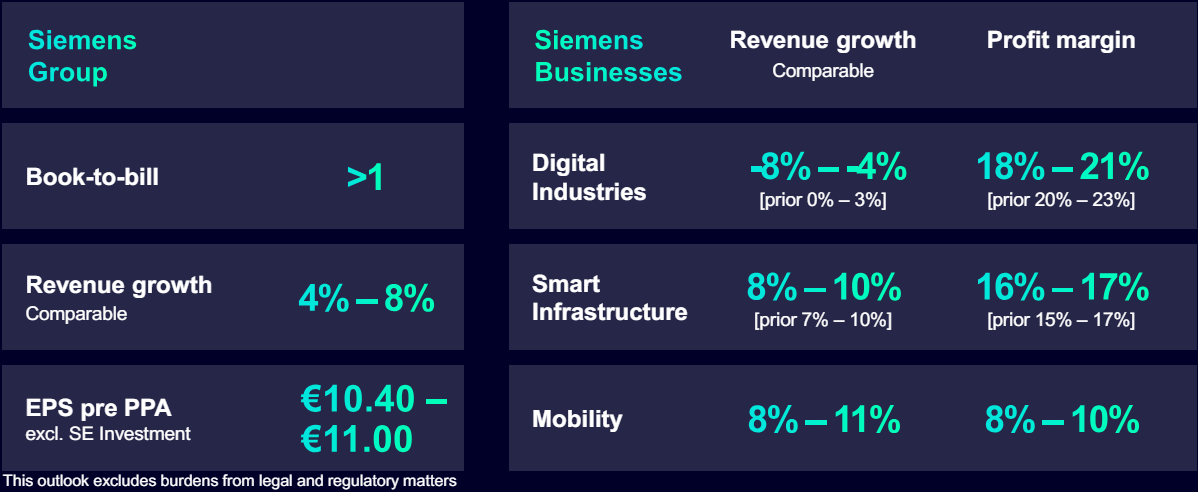
Source: Siemens Q2 2024 Results Presentation
As a result, the company now expects:
- Revenue growth of 6%.
- EPRS pre PPA of about €10.7/share, down 1% Y/Y.
Backlog
Despite the weak topline performance in the first half of the year, Siemens’s 6% growth aspiration for fiscal 2024 is underpinned by stronger order dynamics. The order backlog reached €114 billion, up 3% relative to September 2023. Likewise, the book-to-bill ratio stood at 1.14.
Capital Structure
Siemens ended H1 of fiscal 2024 with a net debt of €41 billion, implying that net debt accounts for 23% of enterprise value. Some 70% of debt is held within Siemens Financial Services. Siemens is also in the process of selling Innomotics, the business encompassing motors and large drives, to KPS Capital Partners for €3.5 billion, with closing expected in H1 2025.
Government Spending Exposure
Unfortunately, Siemens does not break down its sales in terms of end customers, hence a precise amount of government revenue exposure is hard to come by.
That said, some of the company’s business segments are largely reliant on public spending, as explained in the company’s 2023 annual report:
- Mobility segment - the principal customers of Mobility are public and state-owned companies in the transportation and logistics sectors;
- Siemens Healthineers - customer spectrum ranges from public and private healthcare providers, including hospitals and hospital systems, public and private clinics and laboratories, universities, physicians/joint medical practices, public health agencies, public and private health insurers, through to pharmaceutical companies, and clinical research institutes
As a result, considering that the Mobility and Siemens Healthineers segments account for a combined 43% of the company’s H1 2024 revenue, the cumulative government revenue exposure of Siemens is quite significant.
What is more, government-reliant segments grew 4% Y/Y in H1 2024, compared to a 2% decline for private-sector-focused businesses.
Conclusion
Siemens delivered flat Y/Y revenue growth and lower earnings per share despite maintaining robust margins in the core Industrial Business. Looking into the second half of 2024, the company confirmed its previous full-year outlook, with higher revenues and a smaller EPS decline expected for the full year.
The continued growth is underscored by further backlog increases and a book-to-bill ratio of 1.14 in the first half of the fiscal year. At the same time, Siemens continues to exit non-core businesses, with the Innomotics sale targeted for H1 2025.
While government expenditure disclosure is not as detailed as at other large government contractors, some 43% of H1 revenues came from the Mobility and Siemens Healthineers segments which rely heavily on public tenders.
The significance of these two segments is currently growing, with a 4% Y/Y increase in H1 2024, compensating for a 2% Y/Y decline in Digital Industries and Smart Infrastructure.
Given the outlined developments, monitoring the company’s public procurement activity appears to be a smart move that can provide key insights into its financial health.
This article was written by members of TenderAlpha's team and does not serve as a recommendation to buy Siemens or any other stock. TenderAlpha is not receiving compensation for it and we have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
